1. INTRODUCTION OF ALKALOIDS
The term alkaloids (or
alkali-like) was first and foremost proposed by the pharmacist, W. Meissner, in
1819, for the basic nitrogen-containing compounds of plant origin. Ladenburg
defined alkaloids,—‘as naturally occurring plant compounds having a
basic character and containing at least one nitrogen in a heterocyclic
ring.’ With the advent of recent advanced knowledge in the chemistry of
various alkaloids two more inevitable characteristic features were
logically and justifiably added to the definition of alkaloids, namely:
(a) Complex molecular
structure, and
(b) Significant
pharmacological activity.
Furthermore, it was broadly
observed that the basic properties of the alkaloids is solely by virtue
of the presence of N-atom embedded into the five-or six- membered
ring.
Therefore, the alkaloids are
now generally defined as,—‘physiologically active basic compounds of plant
origin, in which at least one nitrogen atom forms part of a cyclic system.’ Even
this definition has a few anomalies as stated below, namely:
(i) Cholines and
Betaines: These two substances have the N-atom in the side chain and not in
the aromatic ring as shown below:
The cholines and betaines
are regarded as simple alkylamines and not classified as alkaloids. They
are designated by some school of thoughts as ‘biological-amines’ or ‘protoalkaloids’.
(ii) Ephedrine: It
has the N-atom only in the side chain and not embedded in the aromatic ring as given
below:
(iii) Piperidine: It
is obtained Piper nigrum (Black Pepper) and does not possess any pharmacological
activity, but has a N-atom in a heterocyclic ring as given below:
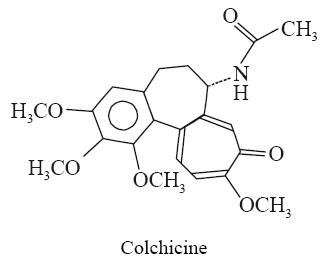
(iv) Colchicine: It
is found to be neither basic nor it contains the N-atom in a heterocyclic ring,
whereas it is considered as an alkaloid due to the fact it possesses distinct
pharmacological activity as shown below:
(v) Thiamine (Vitamin
B1): It confines to the definition of alkaloids but is not regarded
as an ‘alkaloid’ because of its almost universal distribution in living
matter.
Interestingly, alkaloids represent
one of the most important group of chemical constituents occurring in the
entire plant kingdom which exert extremely potent and vital physiological and
pharmacological activities in the human beings. Therefore, it will be
worthwhile to study the alkaloids with regard to the following aspects,
namely:
These various aspects of alkaloids
shall now be discussed adequately in a sequential manner so as to have a
better in-depth of knowledge.
Source:Pharmacognosy And Pharmacobiotechnology By Ashutosh Kar
Source:Pharmacognosy And Pharmacobiotechnology By Ashutosh Kar






0 Comment:
Post a Comment